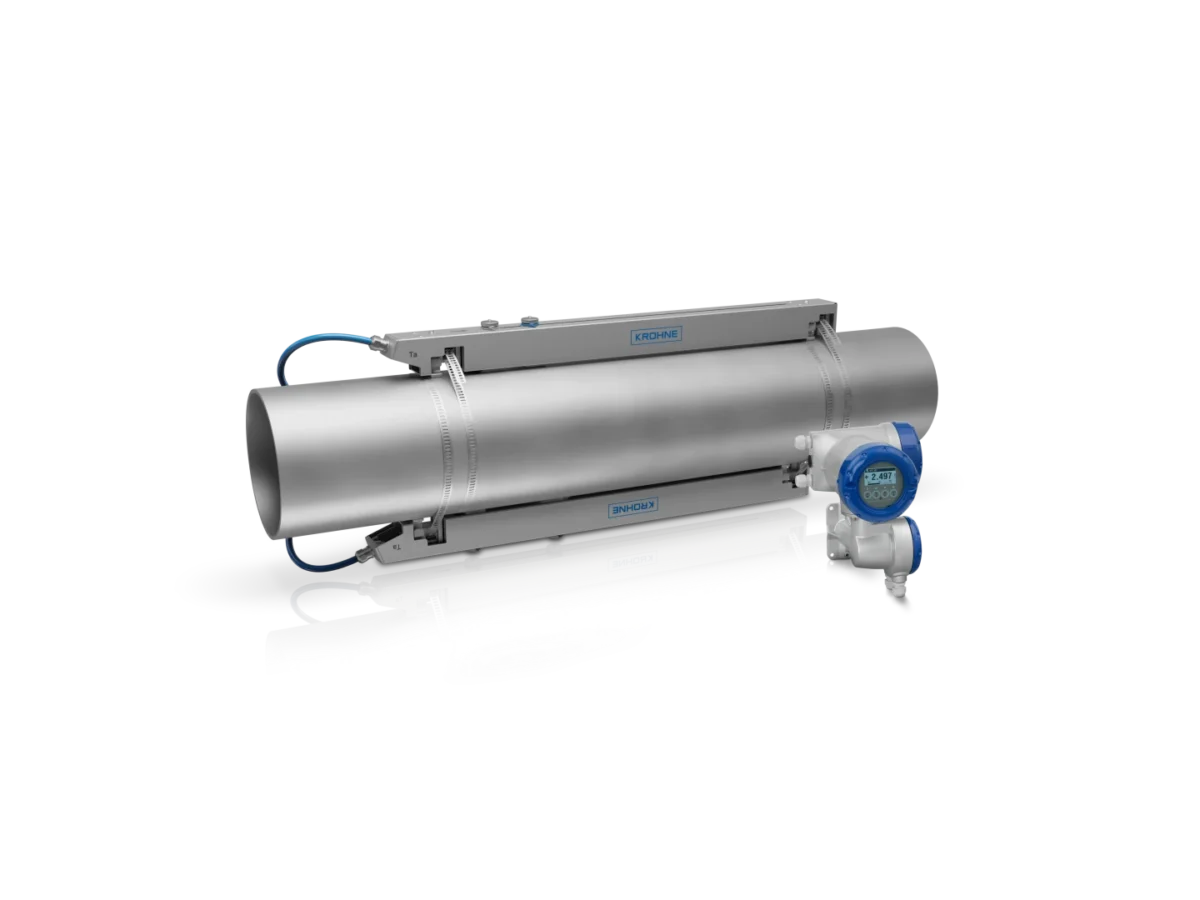

The Art of Sensor Placement
Ultrasonic flow meters provide highly accurate, non-intrusive measurement of liquid flow.
However, their performance depends heavily on where the sensors are installed.
Correct sensor placement ensures precise readings, stable operation, and long-term reliability.
1. Why Placement Matters
Ultrasonic meters measure the time it takes for sound waves to travel through a fluid.
Any disturbance—such as turbulence, bubbles, or an uneven pipe surface—can distort the signal and reduce accuracy.
Positioning sensors in a smooth, straight section of pipe helps maintain a clear acoustic path and consistent readings.
2. Choosing the Right Location
Select a pipe section with minimal bends, valves, or pumps nearby.
A straight run—ideally 10 pipe diameters upstream and 5 downstream of the meter—allows the flow to stabilise before measurement.
Avoid areas prone to vibration or temperature extremes, which can affect signal strength.
3. Preparing the Pipe Surface
Clean, smooth pipe walls are critical for strong ultrasonic transmission.
Remove rust, paint, or debris before mounting the sensors.
A thin layer of acoustic coupling gel ensures optimal contact and reduces signal loss.
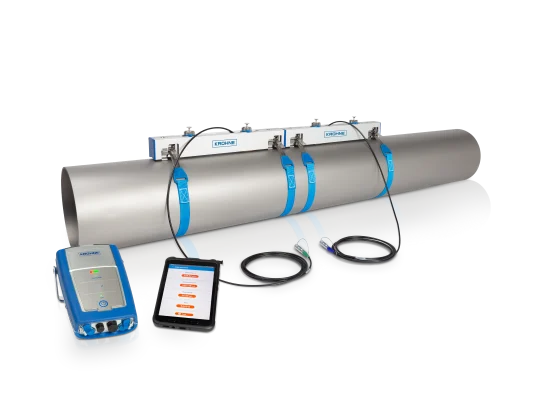
4. Aligning the Sensors
Correct alignment is key.
Sensors must be positioned exactly opposite each other and at the specified angle for the chosen measuring method (e.g., V-method or Z-method).
Use a manufacturer-approved alignment tool or template to maintain precision during installation.
5. Verifying Performance
After installation, perform a calibration or comparison test to confirm accuracy.
Monitor the flow meter over the first few production runs and adjust sensor positioning if readings drift or fluctuate.
Key Takeaway
Ultrasonic flow meters can deliver outstanding accuracy, but only when the sensors are mounted correctly.
By selecting the right location, preparing the pipe surface, and aligning the sensors precisely, operators can ensure reliable, repeatable measurements and long-term performance.
